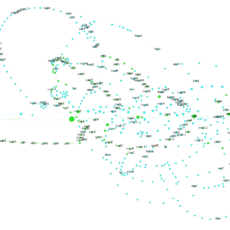
panRGP: a pangenome-based method to predict genomic islands and explore their diversity
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is a major source of variability in prokaryotic genomes. Regions of Genome Plasticity (RGPs) are clusters of genes located in highly variable genomic regions. Most of them arise from HGT and correspond to Genomic Islands (GIs). The study of those regions at the species level has ...
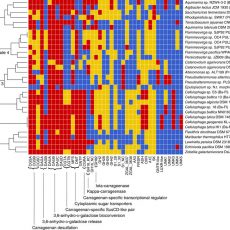
Discovery of the complete catabolic pathway for red algal carrageenans in marine bacteria
Discovery of the complete catabolic pathway for red algal carrageenans in marine bacteria An international consortium coordinated by the Marine Glycobiology team (UMR8227 – CNRS/UPMC) has just published the discovery of the complete system for the utilization of carrageenans, sulfated polysaccharides which are a major component of the cell walls ...

MOPAD: Microorganisms for a sustainable agriculture
The MOPAD project aims to develop biocontrol agent against Fusarium fungi of the soft wheat. Three partners are involved in the project: Biovitis, Vilmorin & Cie and the two labs of the CEA (the LEMiRE and our lab). The LABGeM is involved in the genome analysis of one hundred bacteria ...

Discovery of novel enzymes for the valorization of algal biomass
Algal biomass is underexploited and high value products based on algal polysaccharides and oligosaccharides remain rare. Indeed, commercial enzymes essentially originate from terrestrial organisms which degrade plant biomass and thus are inefficient or inactive on algal biomass. In the context of the emergence of blue biotechnologies in France, the BLUE ...
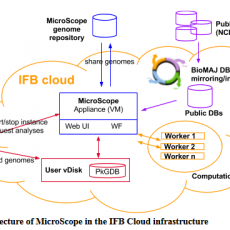
The MicroScope platform raised in the Cloud: toward a Software as a Service for on-demand analyses of microbial genomes (MicroCloud)
MicroScope is an integrated platform to support microbial genomes (re)annotation and comparative analysis. The current project aims at designing a version of the MicroScope platform using Cloud technologies to progressively switch into a Software as a Service (SaaS) distribution mode. This technical evolution will require several adaptations of the current ...
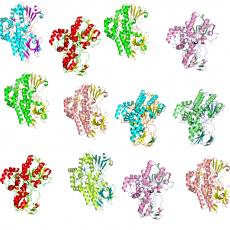
Structural Bioinformatics for unveiling the chemical diversity of enzyme families
A major challenge in modern biology is the discovery of in vivo metabolic or physiological functions of unknown proteins. Our institute has developed an integrated strategy based on in silico prediction of enzymatic activities and in vitro screening of enzymes [1]. As part of this strategy, our team uses structural ...
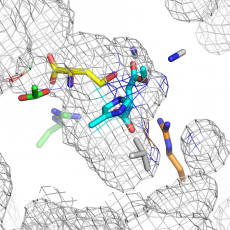
Parallel evolution of non-homologous isofunctional enzymes in methionine biosynthesis
MetX and MetA are two phylogenetically unrelated protein families, but both are implied in the first step of the L-methionine biosynthesis pathway. MetX proteins are known as L-homoserine O-acetyltransferases (HAT), while MetA proteins are generally annotated as L-homoserine O-succinyltransferase (HST). Here we demonstrated that in vitro, over ~100 enzymes, that ...
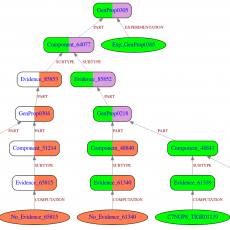
GROOLS: Reactive Graph Reasoning for Genome Annotation
GROOLS (Genomic Rule Oriented Object Logic System) is a bioinformatics software that helps biologists in the evaluation of genome functional annotation through biological processes like metabolic pathways. GROOLS is an expert system that uses paraconsistent logic. It evaluates the completeness and the consistency of predicted functions through biological processes like ...
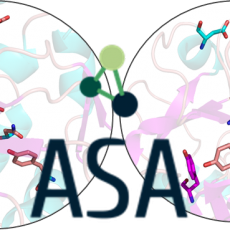
ASA – Active Site Analogies for Enzyme Function Prediction
Nearly 35% of the proteins from large-scale sequencing of microbial genomes are annotated with unknown function. Our objective is to explore, by analogy, active sites from proteins of unknown function using 3D tools in order to suggest enzymatic activities. The first stage involved is the creation of a database containing ...
AMALGAM – Automating microbial genome assemblies
Endless improvements of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) lead to constantly increasing sequencing data that serve various studies such as metagenomics, transcriptomics or WGS projects. De novo assembly of raw data from WGS projects has been a tedious task requiring a strong expertise for a while but the recent development of powerful ...
Mining secondary metabolites in cyanobacterial genomes
Cyanobacteria are an ancient lineage of photosynthetic bacteria, which are prolific producers of secondary metabolites. Hundreds of bioactive compounds with diverse chemical structures , such as toxins and molecules of pharmaceutical interest, have been characterized from cyanobacteria ...
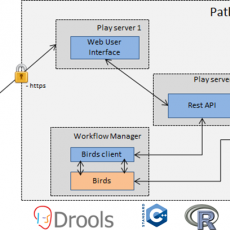
PathoTRACK – Detecting and identifying microbial pathogens in complex samples
In addition to being time consuming and irrelevant for detection of a wide panel of pathogenic targets, current diagnostic methods for pathogens detection (microbial cultures, PCR-RFLP, test strips…) are almost useless in case of complex biological threats (e.g. several pathogens in a mixed sample). Thus, High-throughput sequencing (HTS) becomes undoubtedly ...
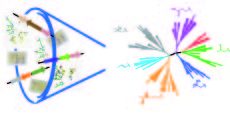
Revealing the hidden functional diversity of enzyme family
There is a massive amount of sequence and structural data available, and the accumulation rate exceeds the pace of functional studies. One way to enhance functional assessment is to mine the available data to inform a strategy that can be applied serially to families of uncharacterized proteins. We have used ...
