Genomics
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology has revolutionized genomics leading to an unrivaled generation of large overloads of omics data ((meta)genomes, (meta)transcriptomes, epigenomes). The use of sequencing machines, which are now smaller in size but capable of generating piles of data faster and at a lower cost, have however raised the challenges of sharing, archiving, integrating and analyzing these data. Efficient and effective pipelines/tools to deal with those increasing amounts of genomics data are therefore needed to store, transfer, analyze, visualize, and generate reports to researchers and possibly clinicians. In this scope, at LABGeM we develop standard as well as innovative tools to get the most of NGS data.

MUDIS4LS project (ESR+/EquipEx PIA3) is leaded by the
French Institute of Bioinformatics (IFB). It is based on 4 technological workpackages and 5 thematic projects (Implementation Studies). It gathers 39 teams from 14 organisations, 4 national data centers, 7 regional data ...

Funded by the French Priority Plan on antibioresistance, the
ABRomics project aims at developing an online community-driven platform to scale up and improve surveillance and research on antibiotic resistance from a One Health perspective.
The platform is made of:
PPanGGOLiN (Gautreau et al. 2020) is a software suite used to create and manipulate prokaryotic pangenomes from a set of either genomic DNA sequences or provided genome annotations. It is designed to scale up to tens of thousands of genomes ...
Background Today, thanks to the development of metagenomics, our knowledge of microbial diversity has greatly changed. Whereas previously cellular organisms were seen more as independent entities, today we know that they organize themselves into complex microbial communities made up of ...
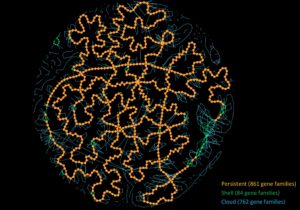
Many comparative genomic studies try to get a grasp on the overall gene content of a species. However, with the current explosion of available genomic data, it becomes more complex to use all-vs-all genome comparison approaches. Over the last years, ...
Functional Annotation
High quality functional annotation is essential for understanding the phenotypic consequences encoded in a genome. We develop several methods to improve protein function predictions. These methods are mainly based on sequence analysis, genomic and metabolic context exploration and structural bioinformatics.
In order to extend the range of tools available to MicroScope users, we aim to develop the platform functionalities dedicated prediction, annotation and exploration of genomic regions. These genomic regions include specialized gene clusters (ie, encoding for secretion systems, CRISPR systems, Biosynthetic Gene Clusters, operons, etc.), phage or GI / ...

We developed a method to classify proteins of a family based on their conserved genomic contexts. Each protein genomic context is compared against all others to determine syntenies. A graph is generated where nodes are input proteins connected by edges when a synteny is observed. Edges weight represent the mean ...







