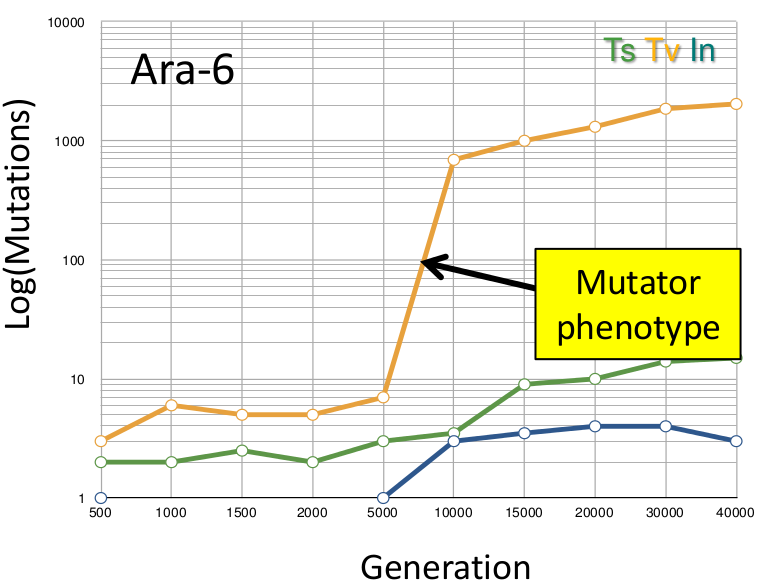
MicroScope – PALOMA (Polymorphism Analyses in Light Of MAssive DNA sequencing) has been designed to use High Throughput Sequencing (HTS) data to detect SNPs and Indels in bacterial populations. To date, our tool has been successfully applied to HTS data generated from long term experimental evolution (1, 2) during which the mutational dynamics of several populations have been monitored (up to 40K generations). Additionnaly, PALOMA Variants Discovery pipeline has also been used to elucidate the pathoadaptation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis during natural evolution by comparing the SNPs/Indels contents obtained by of several contemporary strains of smooth tubercle bacilli (3).
 |
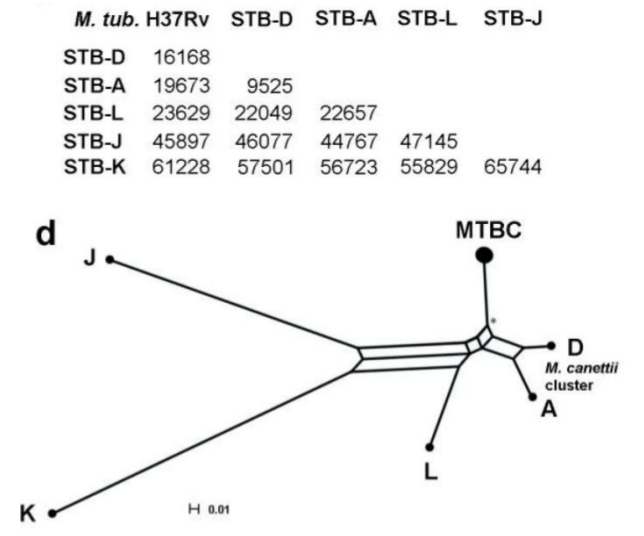 |
| Appearence of a mutator phenotype in a population of Escherichia coli str. B REL606 during a long term experimental evolution. | Network tree based on the comparison of SNPs contents detected in various Mycobacterium (proto)tuberculosis strains. |
Researches metionned above have been recently published in high impact journals such as PNAS or even Science! Moreover, our tool can possibly be used in the frame of MLST studies ( extended to core genome MLST). So, when do you start?
Futher Readings:
1: Wielgoss S, et al.. Mutation rate dynamics in a bacterial population reflect tension between adaptation and genetic load. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 2;110(1):222-7.
2: Plucain J, et al.. Epistasis and allele specificity in the emergence of a stable polymorphism in Escherichia coli. Science. 2014 Mar 21;343(6177):1366-9.
3: Supply P,et al.. Genomic analysis of smooth tubercle bacilli provides insights into ancestry and pathoadaptation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Genet.2013 Feb;45(2):172-9.
