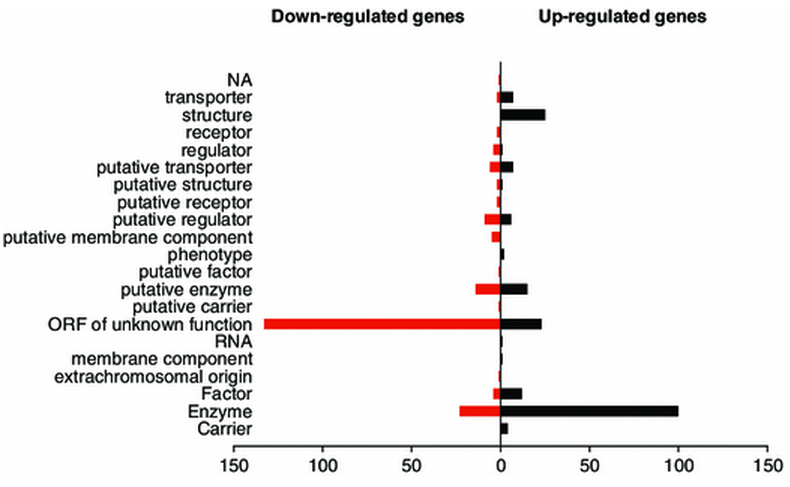
We are proud to announce the publication in Metabolomics (1) of a nice work done in collaboration with our colleagues of the Metabolic Thesaurus Team (CEA//IG/LGBM) in which we used a multi ‘omics’ (RNA-seq, LC/MS, mutants collection) approach to give insights on the metabolic perturbations encountered by the soil bacterium Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 upon a biotic change (shift of sole carbon source from succinate to quinate). All RNA-seq data analyses perfomed during this work were handled with our tool TAMARA (Transcriptome Analyses based on MAssive sequencing of RnAs). In this study, we showed that the expression of more than 12 % of the total number of genes was affected, most of them being of unknown function and that carbon source shift was ultimately reflected in the metabolome.
Futher Readings:
1: Stuani L, et al.. Novel metabolic features in Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 revealed by a multiomics approach. Metabolomics. 2014 Apr 29;1-16.
Research Highlights: TAMARA – When Metabolomics meets transcriptomics…
